 North Korea Increases Aid to Russia, Mos... Tue Nov 19, 2024 12:29 | Marko Marjanovi?
North Korea Increases Aid to Russia, Mos... Tue Nov 19, 2024 12:29 | Marko Marjanovi?
 Trump Assembles a War Cabinet Sat Nov 16, 2024 10:29 | Marko Marjanovi?
Trump Assembles a War Cabinet Sat Nov 16, 2024 10:29 | Marko Marjanovi?
 Slavgrinder Ramps Up Into Overdrive Tue Nov 12, 2024 10:29 | Marko Marjanovi?
Slavgrinder Ramps Up Into Overdrive Tue Nov 12, 2024 10:29 | Marko Marjanovi?
 ?Existential? Culling to Continue on Com... Mon Nov 11, 2024 10:28 | Marko Marjanovi?
?Existential? Culling to Continue on Com... Mon Nov 11, 2024 10:28 | Marko Marjanovi?
 US to Deploy Military Contractors to Ukr... Sun Nov 10, 2024 02:37 | Field Empty
US to Deploy Military Contractors to Ukr... Sun Nov 10, 2024 02:37 | Field Empty
Anti-Empire >>
Indymedia Ireland is a volunteer-run non-commercial open publishing website for local and international news, opinion & analysis, press releases and events. Its main objective is to enable the public to participate in reporting and analysis of the news and other important events and aspects of our daily lives and thereby give a voice to people.
 Fraud and mismanagement at University College Cork Thu Aug 28, 2025 18:30 | Calli Morganite
Fraud and mismanagement at University College Cork Thu Aug 28, 2025 18:30 | Calli Morganite
UCC has paid huge sums to a criminal professor
This story is not for republication. I bear responsibility for the things I write. I have read the guidelines and understand that I must not write anything untrue, and I won't.
This is a public interest story about a complete failure of governance and management at UCC.
 Deliberate Design Flaw In ChatGPT-5 Sun Aug 17, 2025 08:04 | Mind Agent
Deliberate Design Flaw In ChatGPT-5 Sun Aug 17, 2025 08:04 | Mind Agent
Socratic Dialog Between ChatGPT-5 and Mind Agent Reveals Fatal and Deliberate 'Design by Construction' Flaw
This design flaw in ChatGPT-5's default epistemic mode subverts what the much touted ChatGPT-5 can do... so long as the flaw is not tickled, any usage should be fine---The epistemological question is: how would anyone in the public, includes you reading this (since no one is all knowing), in an unfamiliar domain know whether or not the flaw has been tickled when seeking information or understanding of a domain without prior knowledge of that domain???!
This analysis is a pretty unique and significant contribution to the space of empirical evaluation of LLMs that exist in AI public world... at least thus far, as far as I am aware! For what it's worth--as if anyone in the ChatGPT universe cares as they pile up on using the "PhD level scholar in your pocket".
According to GPT-5, and according to my tests, this flaw exists in all LLMs... What is revealing is the deduction GPT-5 made: Why ?design choice? starts looking like ?deliberate flaw?.
People are paying $200 a month to not just ChatGPT, but all major LLMs have similar Pro pricing! I bet they, like the normal user of free ChatGPT, stay in LLM's default mode where the flaw manifests itself. As it did in this evaluation.
 AI Reach: Gemini Reasoning Question of God Sat Aug 02, 2025 20:00 | Mind Agent
AI Reach: Gemini Reasoning Question of God Sat Aug 02, 2025 20:00 | Mind Agent
Evaluating Semantic Reasoning Capability of AI Chatbot on Ontologically Deep Abstract (bias neutral) Thought
I have been evaluating AI Chatbot agents for their epistemic limits over the past two months, and have tested all major AI Agents, ChatGPT, Grok, Claude, Perplexity, and DeepSeek, for their epistemic limits and their negative impact as information gate-keepers.... Today I decided to test for how AI could be the boon for humanity in other positive areas, such as in completely abstract realms, such as metaphysical thought. Meaning, I wanted to test the LLMs for Positives beyond what most researchers benchmark these for, or have expressed in the approx. 2500 Turing tests in Humanity?s Last Exam.. And I chose as my first candidate, Google DeepMind's Gemini as I had not evaluated it before on anything.
 Israeli Human Rights Group B'Tselem finally Admits It is Genocide releasing Our Genocide report Fri Aug 01, 2025 23:54 | 1 of indy
Israeli Human Rights Group B'Tselem finally Admits It is Genocide releasing Our Genocide report Fri Aug 01, 2025 23:54 | 1 of indy
We have all known it for over 2 years that it is a genocide in Gaza
Israeli human rights group B'Tselem has finally admitted what everyone else outside Israel has known for two years is that the Israeli state is carrying out a genocide in Gaza
Western governments like the USA are complicit in it as they have been supplying the huge bombs and missiles used by Israel and dropped on innocent civilians in Gaza. One phone call from the USA regime could have ended it at any point. However many other countries are complicity with their tacit approval and neighboring Arab countries have been pretty spinless too in their support
With the release of this report titled: Our Genocide -there is a good chance this will make it okay for more people within Israel itself to speak out and do something about it despite the fact that many there are actually in support of the Gaza
 China?s CITY WIDE CASH SEIZURES Begin ? ATMs Frozen, Digital Yuan FORCED Overnight Wed Jul 30, 2025 21:40 | 1 of indy
China?s CITY WIDE CASH SEIZURES Begin ? ATMs Frozen, Digital Yuan FORCED Overnight Wed Jul 30, 2025 21:40 | 1 of indy
This story is unverified but it is very instructive of what will happen when cash is removed
THIS STORY IS UNVERIFIED BUT PLEASE WATCH THE VIDEO OR READ THE TRANSCRIPT AS IT GIVES AN VERY GOOD IDEA OF WHAT A CASHLESS SOCIETY WILL LOOK LIKE. And it ain't pretty
A single video report has come out of China claiming China's biggest cities are now cashless, not by choice, but by force. The report goes on to claim ATMs have gone dark, vaults are being emptied. And overnight (July 20 into 21), the digital yuan is the only currency allowed.
The Saker >>
Interested in maladministration. Estd. 2005
 RTEs Sarah McInerney ? Fianna Fail?supporter? Anthony
RTEs Sarah McInerney ? Fianna Fail?supporter? Anthony
 Joe Duffy is dishonest and untrustworthy Anthony
Joe Duffy is dishonest and untrustworthy Anthony
 Robert Watt complaint: Time for decision by SIPO Anthony
Robert Watt complaint: Time for decision by SIPO Anthony
 RTE in breach of its own editorial principles Anthony
RTE in breach of its own editorial principles Anthony
 Waiting for SIPO Anthony
Waiting for SIPO Anthony
Public Inquiry >>
Voltaire, international edition
 Will intergovernmental institutions withstand the end of the "American Empire"?,... Sat Apr 05, 2025 07:15 | en
Will intergovernmental institutions withstand the end of the "American Empire"?,... Sat Apr 05, 2025 07:15 | en
 Voltaire, International Newsletter N?127 Sat Apr 05, 2025 06:38 | en
Voltaire, International Newsletter N?127 Sat Apr 05, 2025 06:38 | en
 Disintegration of Western democracy begins in France Sat Apr 05, 2025 06:00 | en
Disintegration of Western democracy begins in France Sat Apr 05, 2025 06:00 | en
 Voltaire, International Newsletter N?126 Fri Mar 28, 2025 11:39 | en
Voltaire, International Newsletter N?126 Fri Mar 28, 2025 11:39 | en
 The International Conference on Combating Anti-Semitism by Amichai Chikli and Na... Fri Mar 28, 2025 11:31 | en
The International Conference on Combating Anti-Semitism by Amichai Chikli and Na... Fri Mar 28, 2025 11:31 | en
Voltaire Network >>
 international |
environment |
press release
international |
environment |
press release
 Tuesday February 28, 2012 14:43
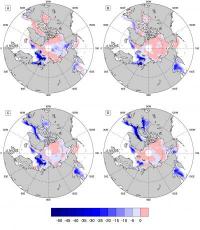
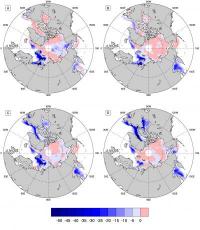
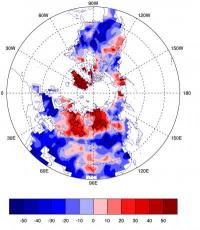
Tuesday February 28, 2012 14:43 by Judith Curry - Georgia Institute of Technology
by Judith Curry - Georgia Institute of Technology























 printable version
printable version

 Digg this
Digg this del.icio.us
del.icio.us Furl
Furl Reddit
Reddit Technorati
Technorati Facebook
Facebook Gab
Gab Twitter
Twitter